The Internet of Things (IoT) has revolutionized the digital landscape, changed how we live and work, and created new security challenges. As the number of IoT devices used in homes and offices increases, there is also a niche for security solutions to tackle these emerging cybersecurity challenges. This is where IoT firewalls come in.
IoT firewall definition
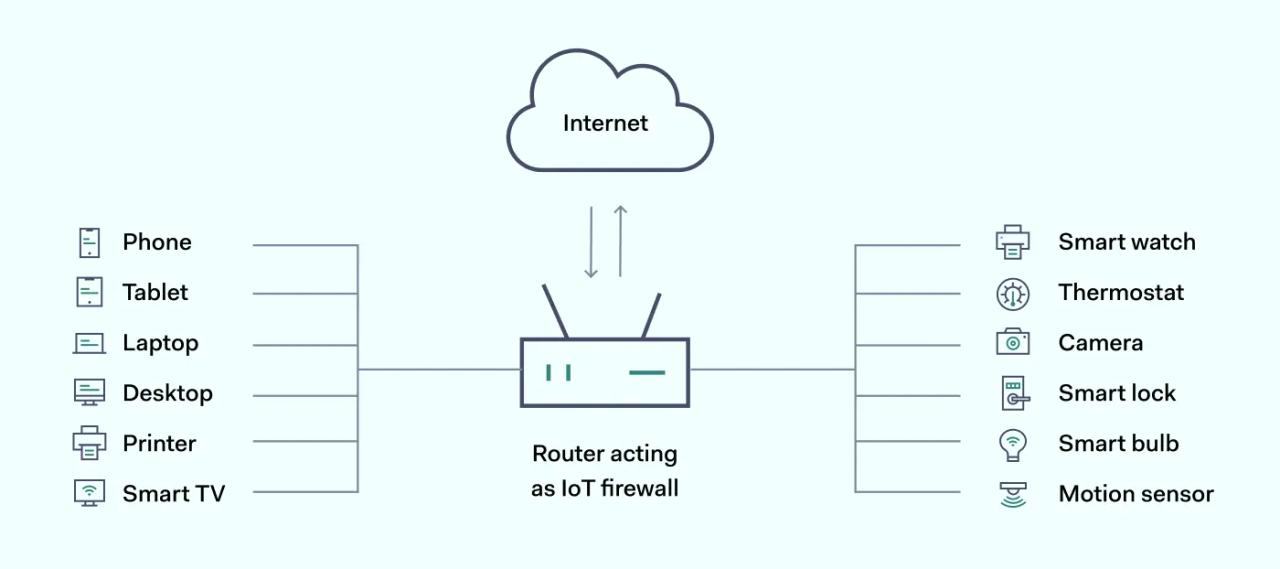
An IoT firewall is a security solution for devices whose traffic patterns fall outside traditional server/client architecture. It's a system that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing traffic based on specific rules. The primary function of an IoT firewall is to prevent unauthorized access to IoT devices and networks.
As most IoT devices generally have a limited range and only connect to specific destinations, this can be used when setting up an IoT firewall. For example, a smart fridge shouldn't be allowed non-HTTPS traffic as other forms of traffic can potentially indicate deviations from normal behavior. They could also precede malicious attacks like denial-of-service (DoS) and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS).
How IoT firewalls work
Similarly to traditional firewalls, IoT firewalls analyze network traffic and determine whether it's authorized or unauthorized. If it's the former, the connection is allowed, but if it's the latter — the connection is denied.
This system can be implemented in two ways.
IoT network firewall
Deployed as a component of network gateway and allowing segmentation options at both macro and micro levels. By using VPN tunnels, these firewalls can encrypt traffic between the gateway and remote servers, which will be handling IoT data adding a security layer.
IoT embedded firewall
Incorporated by the device manufacturer into the operating system of the IoT device itself. Various filtering mechanisms help to ensure safe and secure data transmission and prevent unauthorized access to the device.
In both cases, firewalls can be used for micro-segmentation to create secure zones within a network, shrink an attack surface and limit potential IoT threats.
Benefits of IoT firewalls
Due to their lightweight nature, IoT devices are very hard to secure against online threats. This makes IoT firewalls a beneficial ally that could significantly contribute to the overall organization's business security.
Improved security
IoT firewalls contribute to greater network security by preventing unauthorized access to IoT devices and networks. This can be especially important when IoT devices perform critical business functions. I.e., a manufacturing company could use an IoT firewall to prevent hackers from tampering with it and ensure better business continuity.
Better network visibility
IoT devices can be difficult not only to secure but also to identify. This makes them a considerable business risk as network administrators may not completely understand the organization's network. It's almost impossible to defend against unidentified risks, so an IoT firewall can double as a tracking system and indicate anomalies that could indicate a security breach.
Compliance support
Like other cybersecurity solutions, IoT firewalls can also contribute when pursuing compliance with industry regulations and data privacy laws. In industries where IoT devices are directly used when gathering sensitive client information, IoT firewalls can help to stay in line with data security laws.
Streamline network management
IoT firewalls can be used to segment networks into smaller subnetworks, then various additional access control of security policies could be implemented. As IoT devices are difficult to control and supervise by design, the IoT firewall helps address this design flaw and ensure higher security.
Implementing an IoT firewall
Implementing an IoT firewall is never a one-click solution. This involves multiple steps and requires certain preparations on the business part for the deployment to be smooth and achieve the desired results.
1. Identify the devices
Before implementing the IoT firewall, one of the preparations is identifying all used IoT devices. This may affect the whole planning process: depending on the number of IoT devices or their risks, you may want stricter network segmentation. Let's not forget that devices like security cameras and smart thermostats may also be considered IoT devices.
2. Assess the risks
Each IoT device has a certain amount of risks and vulnerabilities. However, not all pose the same threats to an organization's security. For this reason, it's important to determine what kind of data the device collects and estimate a potential impact if the device is compromised.
3. Select the appropriate firewall solution
Once you understand the internal network's IoT devices better, the next step is choosing a firewall that fits business needs. As discussed previously, the options will be either IoT network firewalls or switching IoT themselves into those with embedded firewalls.
4. Configuration and testing
The chosen firewall should be configured in such a way as to contribute to the organization's security, which may mean different things depending on your business case. This includes rules for traffic filtering and defining access controls for each device. Each configuration should be thoroughly tested in a safe environment to ensure it works as it should.
5. Deploy the firewall
Once the testing is finalized, the IoT firewall can be deployed across the network. Still, it doesn't mean that the process is over. For a firewall to be effective, it's necessary to monitor it regularly and perform scheduled maintenance to ensure that it provides adequate protection against security threats.
Should your business implement an IoT firewall?
An IoT firewall is a crucial cybersecurity component, especially when we see an explosion of IoT gadgets. These devices constitute a significant chunk of connected devices, so they pose significant risks to enterprise security.
By providing an additional layer of protection, IoT firewalls can help protect against cyber attacks, prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data and reduce the risk of compromised IoT devices.